Constructing Your Dream Home Faster with Prefab Methods
- What are the main benefits of using prefab construction?
- How much faster is it to build a prefab home compared to traditional construction?
- What are the cost savings of using prefab construction?
- What types of materials are used in prefab home construction?
- How customizable are prefab homes in terms of design, layout, etc?
- What steps are involved in the prefab home building process?
- What foundations work best for a prefab home?
- How are prefab home modules transported and assembled onsite?
- What are the limitations or downsides of using prefab construction?
- What are the best ways to ensure quality and durability with a prefab home?
The Main Benefits of Using Prefab Construction for Your Dream Home
Prefabricated (or prefab) construction has become an increasingly popular choice for homebuilders looking to construct their dream homes efficiently and effectively. Here are some of the main benefits of using prefab methods:
Faster Construction Timelines
One of the biggest advantages of prefab construction is the ability to significantly shorten project timelines. Since prefab homes are built offsite in a factory using assembly line techniques, construction can happen concurrently with site work. This parallel process reduces on-site labor and allows projects to be completed 30-50% faster than traditional construction.
Modular prefab homes, in particular, can be installed on foundations within a few days. Panelized prefab systems can also be erected quickly. This accelerated schedule gets homeowners into their new homes sooner.
Cost Savings
Faster project timelines translate into big cost savings on both materials and labor. Less on-site construction means fewer expenses for equipment rentals, permits, inspections, site supervision, and contractor overhead.
Factory prefabrication also allows for more efficient use of building materials with less waste. Prefab manufacturers can bulk order supplies for multiple projects, passing quantity discounts on to clients.
The ability to build sections concurrently improves productivity and reduces labor hours. All of this combines to streamline the construction process and cut costs substantially.
High-Quality Construction
Building in a controlled factory setting allows for stricter quality control and workmanship. There is no weather to contend with, so delays are minimized. And specialty equipment can be used for better precision.
The indoor environment also provides worker safety and security for materials. Each section can be inspected before shipping. All of this leads to homes built to higher standards.
Prefabricated components are designed for easy assembly and integration onsite. Connections points are engineered for strength and durability using techniques difficult to replicate onsite. The result is high-performance, quality construction.
Customization Options
Contrary to popular belief, prefab homes can be highly customized to match your unique aesthetic tastes and functional needs. With a flexible panelized system, floor plans can be adapted, and a wide array of finishes and fixtures incorporated.
Today’s prefab manufacturers offer options from modern to traditional home styles. You can usually integrate striking architectural details like cathedral ceilings, skylights, or decorative trims.
Work with your prefab provider early in the process to customize aspects from layout to lighting. Your dream home can be beautifully prefabricated.
Sustainability Benefits
Prefab construction lends itself well to sustainable building practices. The factory setting allows greater control over waste, recycling, and efficient material usage.
Many prefab builders also incorporate energy-efficient construction techniques like:
- Advanced insulation and air sealing
- High-performance windows and doors
- Eco-friendly and locally sourced materials
- Solar panels and renewable energy systems
- Water conservation features
- Non-toxic finishes and adhesives
Prefabrication facilitates quality craftsmanship and integration of systems that make homes environmentally friendly.
Ideal for Challenging Settings
Prefab can be a practical solution when building in remote or difficult locations like steep slopes or dense forests. Since over 90% of construction is completed offsite, minimal clearing or foundation work is required.
Building indoors removes weather constraints for the bulk of a project. And it is much faster to ship pre-assembled units than to truck in traditional construction materials.
Prefab provides reliable high-quality home construction even in the most challenging settings.
Flexible Foundation Options
Prefab homes work with several types of foundation systems. The modules can be attached to a standard poured concrete foundation constructed on site.
But unique foundation solutions are also possible. For example, modular homes can be installed on thickened slab systems with embedded steel for extra reinforcement. Panelized designs can use strip or pier foundations.
With prefab, more possibilities exist based on site conditions, project timeline, and budget. Finding the optimal foundation solution is easier.
Improved Financing Options
For purchasers, using a prefab manufacturer can open up improved financing options compared to a traditional build. Since most of the construction happens offsite, banks recognize there is less risk of delays or problems.
Prefab home companies will have established reputations and track records banks can evaluate. This gives lenders more confidence in funding and can lead to better mortgage rates.
Construction loans are offered by some prefab builders. Down payment and credit requirements may be less stringent as well. Purchasing a prefab can make financing easier.
The many benefits of prefabricated construction demonstrate why it is becoming the preferred homebuilding method for discerning homeowners. Using prefab techniques for your dream home can translate to faster turnaround, lower costs, higher quality, more customization, and flexible financing.
Key Takeaways
- Prefabricated construction shortens project timelines by 30-50% compared to traditional building.
- Building in a factory allows for tighter cost control, quantity discounts, and less waste.
- Indoor assembly and quality control result in superior construction and workmanship.
- Homes can still be adapted with custom layouts, finishes, and architectural details.
- Sustainable features like insulation, energy systems, and non-toxic materials are easily integrated.
- Prefab enables reliable, high-quality home construction even in challenging settings.
- Unique foundation solutions are possible including reinforced slabs and strip footings.
- Prefab builders often offer improved financing options and loan packages for purchasers.
Conclusion
- Faster, cheaper, better quality
- Highly customizable options still possible
- Environmentally friendly construction
- Ideal for difficult locations
- More flexible foundation choices
- Potentially better financing
How Much Faster is Prefab Home Construction?
One of the most touted benefits of prefabricated construction is expedited project timelines compared to traditional stick-built homes. But just how much faster is the prefab process? Here is an overview of the time savings:
30-50% Faster Overall Timeline
Research indicates that on average prefab home construction is 30-50% faster overall compared to standard building. Rather than 18-24 months for a custom site-built home, a similar quality prefab home can be completed in 10-16 months.
For example, a modest 2,000 square foot house would take approximately 16 months using traditional construction. The same home built using modular or panelized prefab can be finished in just 10-12 months.
However, for larger custom homes above 3,000 square feet, the time savings may be less substantial at around 20-30% faster completion. Nevertheless, prefab still produces significant gains.
70% Faster Onsite Time
An even more dramatic contrast is the onsite construction time. The onsite portion of prefab building is approximately 70% faster than traditional methods.
Site-based construction may take 8-12 months for a custom home. But with prefab, this is typically condensed down to just 2-4 months onsite.
That’s because 90% of construction is done in the factory. Foundation work and site prep continue concurrently. So once the home modules or panels arrive, it’s a matter of assembly versus full site building.
How Schedule Compression Happens
There are two major facets of prefab construction that allow faster completion:
Concurrent activity – Site development and foundation work takes place at the same time factory construction is happening. No phase has to wait for previous steps.
Assembly versus building – Rather than full construction onsite, components are simply assembled. This is much faster.
Other factors like indoor factory working, lack of weather delays, and quality control also enable an accelerated schedule.
Modular Schedule Example
To get a better sense, here is an example modular prefab timeline:
- Site prep: 4 weeks
- Foundation poured: 1 week
- Factory build: 12 weeks
- Modules delivered: 1 week
- Onsite assembly: 2 weeks
- Interior finish: 4 weeks
So in about 24 weeks, or just 6 months, the home construction is largely complete. That’s 50% faster than the 12 months a comparable site build would normally take.
Panelized Schedule Example
Panelized systems involve more onsite construction but are still faster. Here is a sample timeline:
- Site prep: 4 weeks
- Foundation poured: 1 week
- Panel fabrication: 10 weeks
- Panel delivery: 1 week
- Panel erection: 6 weeks
- Interior finish: 6 weeks
In 28 weeks, or about 7 months, the house is ready to occupy – still 30% faster than traditional methods.
Significant Time Savings
In both modular and panelized prefab construction, there are major timeline compressions versus stick-built homes. Homeowners can expect to save 30-50% in overall project duration and 70% on just the onsite portion.
Getting into your dream home months faster is one of prefab’s biggest benefits. Skilled prefab specialists help streamline the construction process without sacrificing quality or customization. The faster turnaround makes prefab a very appealing homebuilding option.
Key Takeaways
- Overall prefab home construction is 30-50% faster than traditional building.
- The onsite portion of prefab is 70% faster, taking just 2-4 months.
- Concurrent site/factory work and assembly versus building speed the timeline.
- A 2,000 sq ft modular prefab home can be built in 10-12 months instead of 16.
- Panelized prefab systems take a bit longer but are still 30% faster than stick-built.
Conclusion
- Dramatic 30-50% reduction in overall project timeline
- Just 2-4 months onsite for assembly and finish work
- Concurrent site and factory construction
- Assembly versus full construction onsite
- Still quality construction despite accelerated schedule
Understanding the Cost Savings of Prefab Home Construction
Prefabricated homes provide significant advantages in cost savings compared to traditional construction. By streamlining the building process, prefab lowers expenses in these key areas:
Raw Material Costs
Building in a factory provides economies of scale when purchasing construction materials. Prefab companies order in bulk for multiple projects to get quantity discounts. These savings are then passed along to the client.
Materials also go further since precision cutting and construction techniques reduce waste. One study showed up to 15% less material usage for a prefab home.
With traditional building, materials are ordered piecemeal for one custom home. Waste factors are higher. Prefab maximizes material efficiency.
Labor Costs
Labor is one of the biggest costs of any construction project. Because prefab homes require less on-site construction, fewer contractor hours are needed.
The bulk of skilled labor is in the factory where workers specialize in specific assemblies for maximum productivity. Onsite contractors mainly oversee final assembly and finishes.
One analysis showed prefab labor costs averaging 15-20% lower. For a $500,000 home, that equates to $75,000-$100,000 in savings.
Equipment Costs
With prefab, equipment like cranes or concrete pumps are utilized in the factory construction phase. Minimal specialty gear is needed onsite.
But traditional building requires extensive equipment for all stages of construction. Rental fees, transport, and operation costs add up.
Prefab saves significantly on owning or renting equipment that would sit idle between phases.
Logistics Costs
Transporting complete home sections from factory to site is more efficient than making multiple deliveries of lumber, concrete, and other supplies to a worksite.
And modular sections can be stacked tightly into containers for transport, using space efficiently. This reduces shipping costs.
Fewer truckloads and shipments means lower fuel and driver costs as well. Better logistics control brings expenditures down.
Overhead Costs
A long project timeline with traditional construction means higher general overhead costs. There are extended site supervision hours, temporary utilities, trailer rentals, and more.
But with prefab, shorter timelines mean less expense on these overhead items. The bulk of supervision and support happens at the factory, further reducing costs.
Financing Costs
Prefab construction can also lower financing costs. Since most work happens offsite, banks recognize there is less risk of delays or cost overruns.
This qualifies buyers for improved financing terms in some cases. Lower interest rates and better loan packages make financing prefab more affordable.
In total, prefabricated homes can cost 10-20% less to build than comparable site-built custom homes. For a $500,000 house, that represents $50,000-$100,000 in savings – enough to pay for luxury finishes and features.
Key Cost Drivers
The main factors producing cost savings with prefab include:
- Bulk material discounts
- Less material waste
- Reduced labor hours
- Minimal equipment needs
- Lower transportation costs
- Shorter timeline overhead
- Improved financing rates
Cost Savings by System
Cost savings will vary slightly depending on the type of prefab system:
- Modular: 15-20% savings
- Panelized: 10-15% savings
- Kit of Parts: 10-12% savings
But all methods benefit from the efficiencies of prefabrication versus traditional stick-built construction.
Economies of Scale
Larger custom homes above 3,500 square feet may see slightly less cost savings in percentage terms. But because of economy of scale, the gross dollar savings are quite substantial.
Prefab still offers significant advantages for budget-conscious luxury custom home buyers looking to maximize value.
With its various efficiencies and supply chain advantages, prefab is proven to reduce overall construction costs dramatically, making it a smart budget choice.
Conclusion
- 10-20% lower costs than traditional building
- Savings from bulk material discounts
- Lower labor, equipment, logistics overhead
- Improved project financing terms
- $50-$100k savings on a $500k home
- Budget-friendly custom home option
Quality Materials Used in Prefab Home Construction
Prefabricated homes not only save money, but also incorporate high-quality durable materials to create structures built to last. Here are some of the main construction materials used:
Structural Timber Frames
Sustainably sourced lumber is used to construct structural frames for modular units or panelized wall systems. Kiln-dried lumber avoids issues like warping or mold.
Advanced milling equipment produces precision-cut timber elements ready for rapid assembly. Durable engineered wood beams and columns add strength.
For long-lasting performance and resilience, cedar, cypress, or treated pine are common frame choices. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) integrate insulation.
Steel Structural Members
As an alternative to wood framing, galvanized steel studs and structural members are sometimes used. Steel offers:
- High precision and consistency
- Termite/mold/mildew resistance
- Non-combustibility for fire safety
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio
Steel panels with insulated cores provide structure, insulation, and shear resistance in one durable unit.
HIgh-Performance Insulation
Insulation is what gives homes comfort, energy efficiency, and acoustic isolation. Prefab builders use:
- Fiberglass batts with sound-dampening properties
- Rigid foam boards for added insulation value
- Spray foam insulation that seals cracks and gaps
- Cellulose loose-fill made from recycled materials
Advanced sealing techniques ensure there are no gaps or thermal bridges. This maximizes insulation performance.
Moisture Barriers
Proper moisture protection prevents leaks, condensation issues, and moisture damage in walls and roofs.
- House wrap water-resistive barriers
- Waterproofing membranes for wet areas
- Rainscreen systems that allow drainage
- Vapor retarders that limit diffusion
Multi-layered barriers provide redundant moisture protection.
High-Efficiency Windows
Energy efficient windows with insulated low-E glass, argon gas, and warm edge spacers reduce solar heat gain and heat loss. Composite frames offer durability.
Larger window units are possible through precise prefabricated wall openings. This increases daylighting. Windows promote indoor-outdoor connections.
Durable Exterior Finishes
Low-maintenance exterior finishes enhance aesthetics, protect against weathering, and reduce lifetime costs.
- Fiber cement siding, planks, and panels
- Composite wood-plastic cladding
- Brick, stone, or metal accent panels
- Standing seam metal roofing
Prefab lets buyers select premium exterior material options.
Prefabricated homes allow the use of high-performance structural, insulating, weather-resistant materials for maximum quality, resilience, and longevity.
Conclusion
- Precision-milled timber framing
- Galvanized steel structural components
- High-performance insulation types
- Redundant moisture barrier systems
- Energy efficient window units
- Durable, low-maintenance exterior finishes
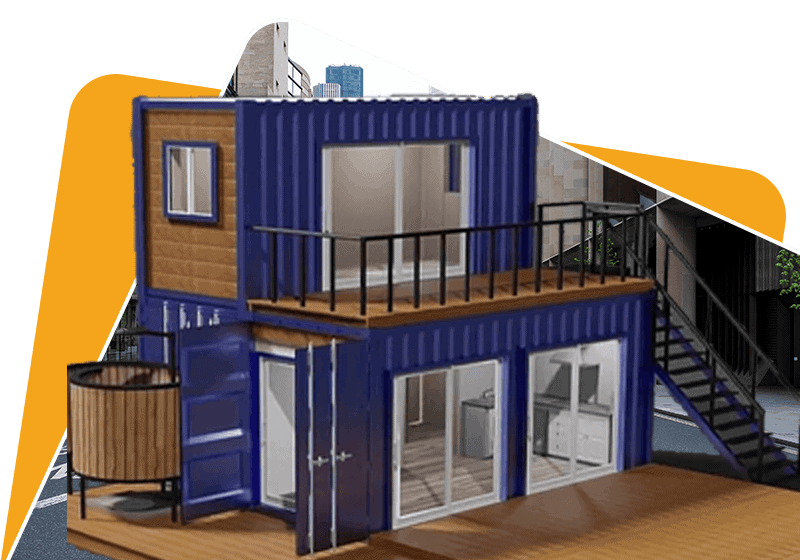
The Customization Potential of Prefab Homes
Prefabricated homes are sometimes seen as cookie-cutter designs with limited flexibility. However, today’s quality prefab builders offer abundant customization in these areas:
Floor Plan Options
Prefab floor plans include open concept single-story designs, multi-level plans, and options with multiple wings or sections. Plans can be tailored to suit:
- Number of bedrooms and bathrooms
- Spaces like a home office or gym
- Custom storage and closet solutions
- Flow preferences and indoor/outdoor connections
With a panelized system, nearly any floor plan is possible. Layouts accommodate disabilities.
Interior Finishes
Homeowners have extensive choice regarding:
- Flooring like hardwood, tile, or carpet
- Cabinetry styles from modern to farmhouse
- Plumbing and lighting fixtures
- Appliances and smart home systems
- Paint colors, wall finishes, and trims
- Bathroom and kitchen backsplashes
- And more based on your taste
Architectural Detailing
Unique architectural elements like rafter tails, decorative gables, dormers, columns, and trim accents can be incorporated. This allows designs like:
- Craftsman style bungalows
- Rustic mountain cabins
- Contemporary cubist designs
- Mediterranean or Tuscan villas
- And anything in between
Roof Styles
Choose from gabled, hipped, shed, or exotic roofs. Options like dormers, skylights, and complex multi-level roofs are possible.
Rooftop solar systems can be integrated into the waterproofing system. Roofing material choices range from asphalt to metal.
Facade Options
The exterior facade can be customized through:
- Mix of siding materials and patterns
- Fun colors and textures
- Corner boards, frieze, and trim accents
- Shutters, flower boxes, and ornamental railings
- Masonry elements like brick or manufactured stone
- And more to achieve your desired style
Today’s quality prefab builders allow extensive customization while still providing the benefits of offsite construction. The days of boxy cookie-cutter prefabs are over.
Conclusion
- Ability to adapt floor plans as needed
- Personal selection of all interior finishes
- Unique architectural detailing possible
- Custom roof shapes, elements, and materials
- Mix and match facade options for your style
The Step-By-Step Process of Prefab Home Construction
Interested in having your dream home prefabricated? Here is an overview of the typical construction process:
Design Phase
This initial phase involves deciding on:
- Number of bedrooms, bathrooms, and other spaces needed
- Overall home size and square footage
- Architectural style preferences
- Customizations desired
- Budget parameters
With your wishlist in mind,floor plans are drafted and 3D renderings created. Your prefab builder provides design expertise and recommendations.
Engineering Phase
Once the preliminary design is approved, engineers generate technical drawings, determine structural loads, and specify materials needed.
They design structural wall panels, roof trusses, and other prefabricated components considering transportation limitations.
Engineers ensure the home meets or exceeds all relevant building codes and standards.
Production Phase
This is where the bulk of construction happens – at the prefab factory.
- Shop drawings guide each manufacturing station.
- Walls, floors, and roof sections are framed and insulated.
- Connections points and openings are prefabricated.
- Electrical, plumbing, HVAC, and fire protection systems are roughed-in.
- Exterior sheathing and moisture protection added.
Logistics Phase
The completed modular sections or panelized components are loaded onto trucks for delivery.
Specialty trailers safely transport units. Wide loads may need pilot vehicles and removable light poles enroute.
Local permits, road closures, and police escorts may be arranged. The logistics team oversees safe, on-time delivery.
Onsite Assembly
After foundation and utilities are prepped, the prefab components arrive.
Cranes lift sections into place. Crews interconnect units and tie into utilities.
Panelized buildings are erected and structural connections made. Weather-tight building enclosure achieved.
Finish Phase
Interior and exterior finish work happens concurrently.
Crews complete:
- Flooring, trim, doors
- Cabinetry, fixtures, appliances
- Painting, blinds, accessories
- Driveways, walks, landscaping
With coordination between your project team, site contractors, and prefab supplier, the manufacturing and building process results in your dream home efficiently delivered.
Conclusion
- Initial design and customization input
- Engineering for structural integrity and code compliance
- Factory prefabrication of modules or panels
- Logistics plan for safe delivery
- On-site assembly and structural completion
- Interior and exterior finish work
Choosing the Best Foundation for a Prefab Home
Prefabricated homes can be installed on several foundation types to suit the site, construction style, and budget. Here are some top options:
Poured Concrete
A traditional poured concrete perimeter foundation works well for modular prefab homes. Concrete offers:
- Long-term stability and minimal movement
- A smooth surface for precise module joining
- Excellent load-bearing capacity
- Permanence and rot/pest resistance
Footings are sized based on soil conditions. Walls are formed and poured, then backfilled. If basement space is desired, walls are waterproofed.
Prefab installers will bolt home modules directly to the concrete.
Reinforced Concrete Slabs
Concrete slab foundations are common in temperate climates. They offer similar strengths as perimeter foundations.
Reinforcing bars (“rebar”) cast into the slab prevents cracking. Thicker edge areas provide stability. Insulation under the slab helps moderate soil temperatures.
For modular construction, slabs may be further strengthened with embedded steel plates. These act as connection points to bolt modules to.
Pier and Beam
This foundation style uses spaced concrete piers, usually 1-2 feet thick, with steel rebar. Grade beams connect the tops of piers in a grid.
The prefab structure is then erected and floor framing attached to the beams. More piers may be added under major structural elements.
Piers work well on sites with expansive soils. They allow for some ground movement. Useful in flood-prone areas too.
Pile Foundations
Where poor soil or really uneven terrain exists, pilings may be used. This involves driving long steel or concrete poles into the ground to bearing soil or bedrock.
A deep pile cap then connects a group of pilings. Beams rise from the cap to support floor slabs or directly connect to modules.
While costly, piles allow construction on otherwise unusable sites. They can also raise homes above flood levels.
Strip Footings
Simple strip footings can work for panelized prefab systems with wood frame walls bearing directly on the foundation.
Trenches are excavated, forms erected, and concrete poured to create continuous footings under each wall.
Depth is based on frost line and soil strength. Light frame walls are anchored to the footing with bolts.
With prefab construction, foundation requirements are well-defined in advance. This allows selection of the optimal foundation type for your site and home.
Key Selection Factors
Choosing the ideal foundation involves assessing:
- Soil conditions and slope
- Local frost depth and climate
- Flood and seismic risk
- Construction style and loads
- Basement desires
- Initial and long-term costs
The prefab builder will guide appropriate foundation selection and design.
Conclusion
- Poured concrete for modular homes
- Reinforced slabs in temperate climates
- Pier and beam useful on expansive soils
- Pilings for problematic sites
- Strip footings for panelized buildings
How Prefab Home Modules and Components Are Delivered
Once prefabricated home sections are complete, the next vital step is carefully transporting them from the factory to the final site. This requires thorough planning and coordination.
Overview of Transportation Logistics
The logistics process involves these key elements:
Permitting – Securing necessary transportation permits for wide or overweight loads. Police escorts and temporary removal of road signs, lights, or utilities may be required.
Route Planning – Determining the optimal delivery route considering road widths, height clearances, bridge capacities, and work-around options.
Rigging – Lifting, loading, and bracing wall panels or whole modules using cranes and specialty equipment at the factory. Components are strapped down securely to flatbed trailers.
Transport – Trucking units via predetermined routes using proper pilot/escort vehicles. Additional route prep like filling potholes or trimming trees may be needed.
Unloading – On site, cranes lift units carefully off trailers and either temporarily store them or install them onto the prepared foundation system.
Modular Home Transportation
Modular units are typically fully enclosed homes with floors, walls, roof, and often interior finishes. They measure 14-16 feet wide and up to 80 feet long.
Multi-axle extendable trailers carefully transport each module. Tractor trucks capable of heavy loads are used.
Road travel usually happens at night to minimize impact on local traffic. Police manage needed road or lane closures.
Panelized Home Transportation
Panelized wall systems, roof trusses, and floor boxes are lighter and can use standard flatbed trailers. But lengths may still exceed regulated road limits.
Panels are commonly stacked flat on trailers. Some designs allow nested stacking to maximize loads. Tarps protect from weather and debris.
Final Mile Logistics
The final delivery from main roads to the building site is known as the “last mile.” This often involves small rural roads.
Temporary improvements like widening sharp corners may be required. Crews need to trim overhanging trees as well.
Sections are either craned directly into place or stored onsite until needed for installation. Logistics teams ensure efficient, safe end delivery.
Well-orchestrated transportation logistics are key to delivering prefab home sections damage-free while minimizing community impact.
Conclusion
- Advanced permitting, route planning, rigging
- Police escorts and utility/road modifications
- Multi-axle extendable trailers for modular
- Standard flatbeds for panelized but oversize
- Improvements to local roads for final delivery
- Just-in-time installation or temporary storage
Limitations and Downsides to Consider with Prefab Homes
While prefabricated homes offer faster, more affordable construction, there are some limitations and downsides to weigh as well:
Design Constraints
The modular construction process imposes some design restrictions. Dimensions are limited by road transportation regulations.
Plumbing and duct runs need to be contained within a module. Openconcept designs across units can pose challenges.
Complex rooflines and architectural elements may not be possible based on structural needs and assembly methods.
However, panelized systems allow more design flexibility with fewer long-span constraints.
Customization Limits
Modular prefab systems are not as customizable once main unit construction begins. Layout or finish changes can be costly and cause delays.
So modifications need to be finalized earlier in the process, with less opportunity to make adjustments once built.
Again, panelized designs allow more adaptability later in the schedule.
Upfront Planning Needs
A higher level of upfront planning is required with prefab. All design decisions must be made very early before factory construction commences.
Last-minute layout tweaks or material changes are not feasible. Time is needed to engineer each component.
With stick built homes, there is more flexibility to alter plans mid-stream. Prefab requires decisive vision early.
Site Constraints
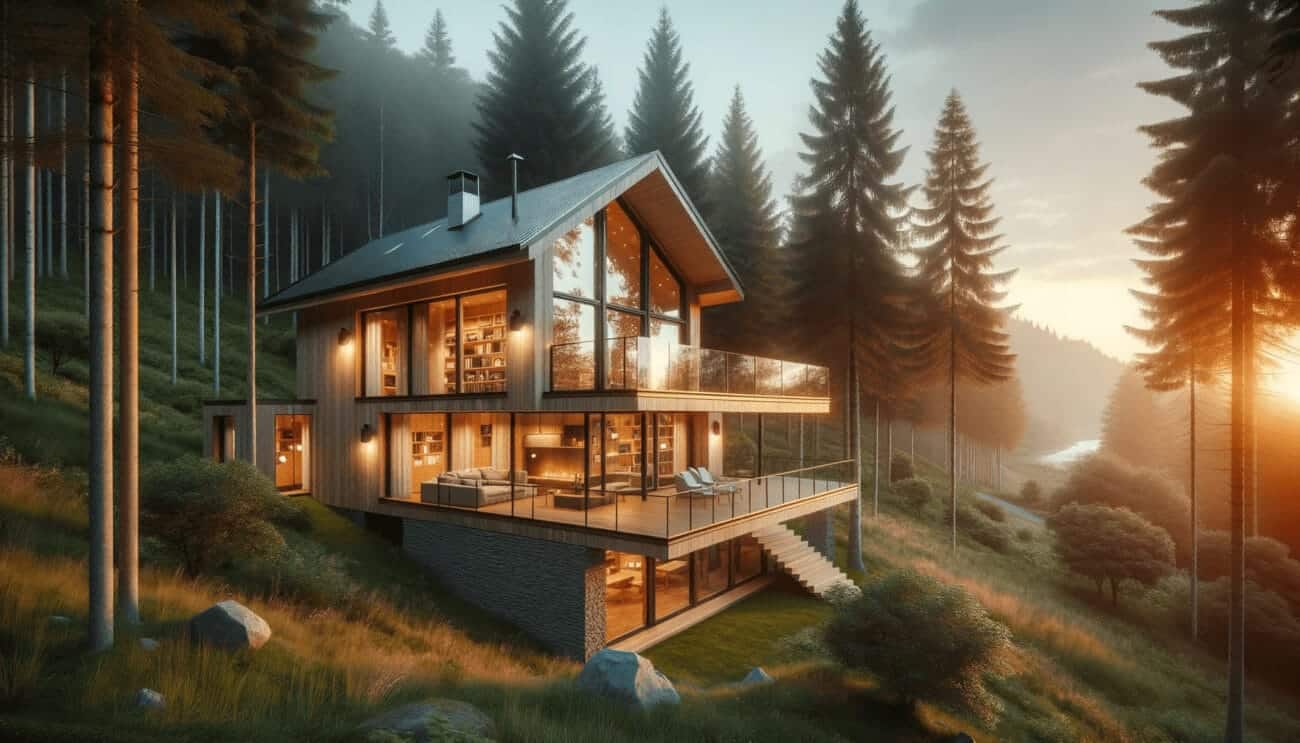
Ideal sites are flat, open, and easily accessed by road. But many dream home locations are hillside, forested, or remote plots.
Extra site prep and grading may be needed for prefab modules to work. Overhead vegetation clearance, temporary roadways, and crane access are common requirements.
Panelized systems are better suited to constrained sites, but access is still a factor.
Single Source
With prefabrication, you are reliant on one company for design, manufacturing, logistics, and assembly. Quality depends on their expertise.
If after-sale issues occur, remedies may be limited. Traditional construction allows sourcing from many vendors.
Thoroughly vet any prefab provider on qualifications, experience, warranties, and client reviews before committing.
Prefab requires some design compromises and site constraints. But reputable prefab builders can overcome many limitations through quality engineering and construction.
Conclusion
- Earlier decision-making required
- Less flexibility once manufacturing begins
- Common design constraints to consider
- More complex site needs for access
- Reliant on single source for quality
How to Ensure Quality and Durability with a Prefab Home
Prefabricated homes differ from traditional construction, so extra steps should be taken to ensure your prefab home is top quality and built to last. Here are some tips:
Partner with a Reputable Builder
Vet prefab builders thoroughly. Seek companies with:
- A long, proven track record
- Extensive experience with complex projects
- An in-house engineering team
- Manufacturer certifications like ISO-9001
- Membership in trade organizations like MBI
Reviews from past clients provide insight on responsiveness and service quality after sale.
Evaluate Construction Methods
Look for structures built with sturdy framing and advanced sealing techniques like:
- Screwed AND glued fastening
- Seamless air barriers
- Redundant waterproofing
- Robust connections between modules/panels
This delivers durable, resilient buildings that stand the test of time.
Confirm High-Performance Materials
Specify durable, mold/rot/termite resistant materials:
- Kiln-dried framing lumber
- Galvanized steel connectors
- Closed-cell spray foam insulation
- Moisture-resistant exterior sheathing
- Composite exterior claddings
Avoid cheap products prone to early failure or leaks.
Demand Stringent Testing
The factory setting allows thorough testing of components before shipment:
- Structural load tests of frames and panels
- Air infiltration measurements
- Thermal imaging scans
- Water testing of enclosures
- Electronic systems function checks
This reduces onsite troubleshooting and ensures quality.
Verify Structural Engineering
Engage an independent engineer to review the proposed structural systems, load paths, and connections.
Verify design assumptions match your specific site parameters like wind, seismic zones, and soil type.
Solid engineering prevents issues down the road as the building ages and settles.
Plan for Onsite Inspections
Arrange follow-up site visits at key construction stages for your own quality assurance checks. Bring in a specialist inspector if desired.
Thoroughly check foundation, utility, envelope, and structural connections for any defects before covering up.
Keep quality assurance as a priority throughout the prefab design, manufacture, and assembly process to maximize your home’s longevity.
Conclusion
- Select only top prefab builders with proven records
- Scrutinize construction methods and materials used
- Demand extensive factory testing
- Verify independent structural engineering
- Perform thorough onsite inspections at milestone stages
Key Takeaways
Prefabricated construction offers dramatic advantages in speed and cost savings versus traditional building. However, prefab is still a comprehensive process involving:
- Multiple design iterations to maximize customization
- Structural engineering ensuring safety and code compliance
- Highly controlled factory assembly of modules or panels
- Complex logistics to transport units to site
- Coordination of foundation, utility, and assembly work
- Finish carpentry and detailing work onsite
Despite drawbacks like design constraints or upfront planning needs, prefab homes provide faster occupancy along with the quality and customization today’s homeowners demand. With careful process management and partnering with experienced prefab specialists, virtually any dream home can be realized through offsite construction.
Prefab has moved far beyond basic cookie-cutter designs to offer the innovative construction approaches and luxury finishes that discerning homeowners expect. Construction timelines under a year are possible while still delivering stunning, highly customized homes built to last using advanced methods. As technology progresses, the possibilities of prefabrication will continue expanding.
Conclusion
- Prefab combines speed and customization
- Engineering expertise ensures structural integrity
- Controlled factory production increases quality
- Logistics are key to safely delivering units
- Foundation and site prep precede assembly
- Finish work adds beauty and functionality
- With skilled partners, prefab limitations can be overcome
- Prefab innovations enable faster luxury homebuilding
Kontraktor Rumah Kabin
Rumah Kabin Murah
Rumah Kontena Vs Rumah Kabin
Rumah Kabin Pasang Siap
Senarai Harga Kabin di Malaysia
Heavy Duty Cabin
Light Duty Cabin